Actuary Job Description
What is an Actuary?
Curious what a typical actuary job description looks like? An actuary is a professional who uses mathematics, statistics, and financial theory to predict financial outcomes for businesses and individuals.
Actuaries are essential to the function of many businesses, as they help organizations make informed decisions about managing and mitigating risk.
They typically work for insurance companies, but may also work for banks, pension funds, consulting firms, and government agencies.
For example, an actuary might help a life insurance company set premiums that will cover the expected costs of future claims from events like death and disability.
What Does an Actuary Do?
Actuaries are trained in probability and statistics. They use this knowledge to calculate the likelihood of future contingent events, like the probability of a group of cars out of a fleet of insured vehicles suffering hail damage. This information helps their clients (usually insurance companies) make informed decisions about managing risk (like setting the correct car insurance premiums).
Actuaries typically work in the insurance industry and evaluate financial risk. They are experts in evaluating the likelihood of events that could occur in the future using their analytical math skills. They can also evaluate how to reduce the likelihood and impact of undesirable events.
In the example above, an actuary could advise the insurance company to send out weather warning notifications to its insured drivers. In this way the drivers can avoid being caught in severe weather conditions that could lead to car damage and subsequent claims.
Their work is essential to the insurance and finance industries, and they are in high demand.
Role of an Actuary
An actuary is a professional who uses mathematical skills and statistical analysis to assess financial risks.
Their work is essential in helping businesses and organizations make informed decisions about risk management. For example, an actuary’s job description could be to help a bank determine the probability of its clients defaulting on loans and credit card payments.
They help companies in the insurance industry ensure payment of future benefits by ascertaining cash reserves and premium rates needed. This not only protects the insurance company from going under, it also ensures clients are appropriately covered against risky events, which benefits the individual and society as a whole.
A variety of stakeholders such as shareholders, company executives, government officials and other stakeholders would expect an actuary to explain complex technical matters and help determine company policies. This means, as you can probably gather, that actuaries require excellent communication skills. They need to take subject matter expertise and explain these concepts in layman’s terms.
As part of an actuary’s job duties, he or she would review, design and help administer pension plans, insurance policies or annuity plans by calculating premiums and financial soundness.

Actuaries often work with complex data sets and use their skills to assess the likelihood of future events, and to help businesses and organizations make decisions about risk management. The need to manage and work with big sets of data, has meant that the job description of an actuary has become more and more intertwined with that of a data scientist.
Actuary Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of an actuary vary depending on the industry they work in.
As mentioned above, actuaries can work in various industries ranging from insurance work to venture capital to banking.
Despite the varying industries, there are some common duties actuaries perform in the companies they work for. An actuary’s job description typically includes:
- analyzing data to identify trends,
- developing models to predict future events,
- understanding the industry’s ecosystem and its various stakeholders,
- using mathematical skills and statistical analysis to assess financial risks, and
- communicating findings to a non-technical audience.
For example, an actuary might identify, from the data of a property insurance portfolio, that there are more developments and home ownership close to flood-risk areas. They can combine this knowledge with statistics on climate risk, global warming and rising water levels to assess the risk of higher future claims for the insurance company.
In addition to their technical responsibilities, a key part the actuary job description is to clearly relay their findings to stakeholders who don’t have a technical background.
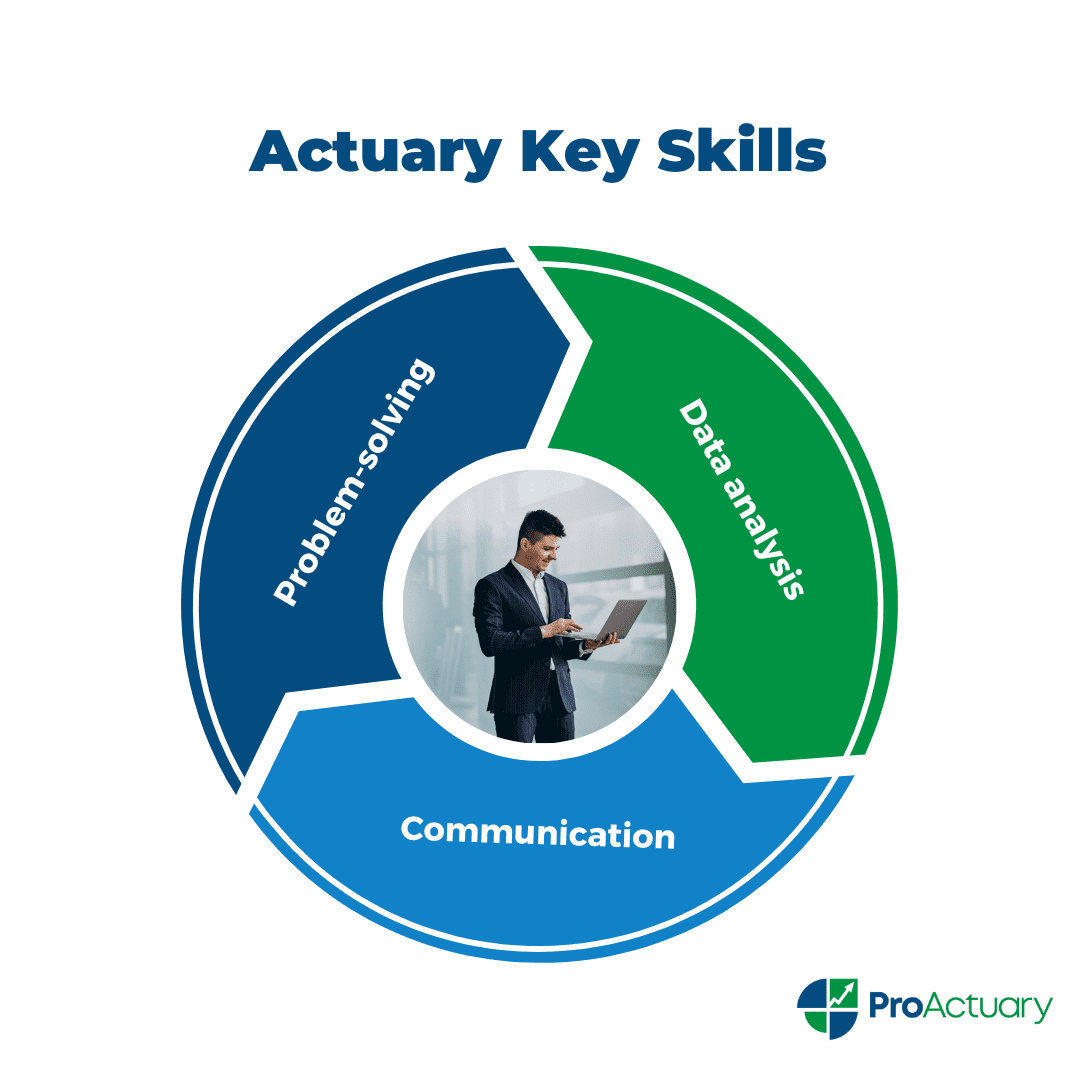
Actuary Skills
An actuary’s work requires them to have strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
They must be able to interpret statistical data and identify trends. They also need to be able to communicate their findings to others in a clear and concise way. The difference between an mediocre actuary and a great actuary is their ability to communicate effectively.
Because of the nature of their work, actuaries must be able to work well under pressure and handle stress. Working under tight deadlines and making significant decisions for the company are part of the responsibilities job description of an actuary.
Actuary Career Path
In order to become an actuary, actuarial students should acquire a bachelor’s degree in mathematics, actuarial science, or business studies.
Coursework in statistics, economics, computer science, mathematics, risk management, calculus, and corporate finance provide an excellent foundation for actuarial exams and actuarial analyst jobs.
After completing their degree, actuarial students can join a number of different companies in the financial services sector, including insurance firms, banks, pension funds and investment management firms, amongst others.
While working as actuarial analysts (the starting point on the road to become an actuary), aspiring actuaries must pass a series of actuarial exams administered by their country’s actuarial body. Examples of these professional bodies include the Society of Actuaries or Casualty Actuarial Society in North America or the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries in the United Kingdom.
These actuarial exams are often completed in conjunction with working full time and have low pass rates (sometimes as low as 30-40%) showing how difficult it is to complete the long road to become a qualified actuary.
Following their exams, actuaries form part of their country’s professional body and take on more responsibility in their roles at work. The actuary’s job duties then include managing junior team members and leading projects in their departments.
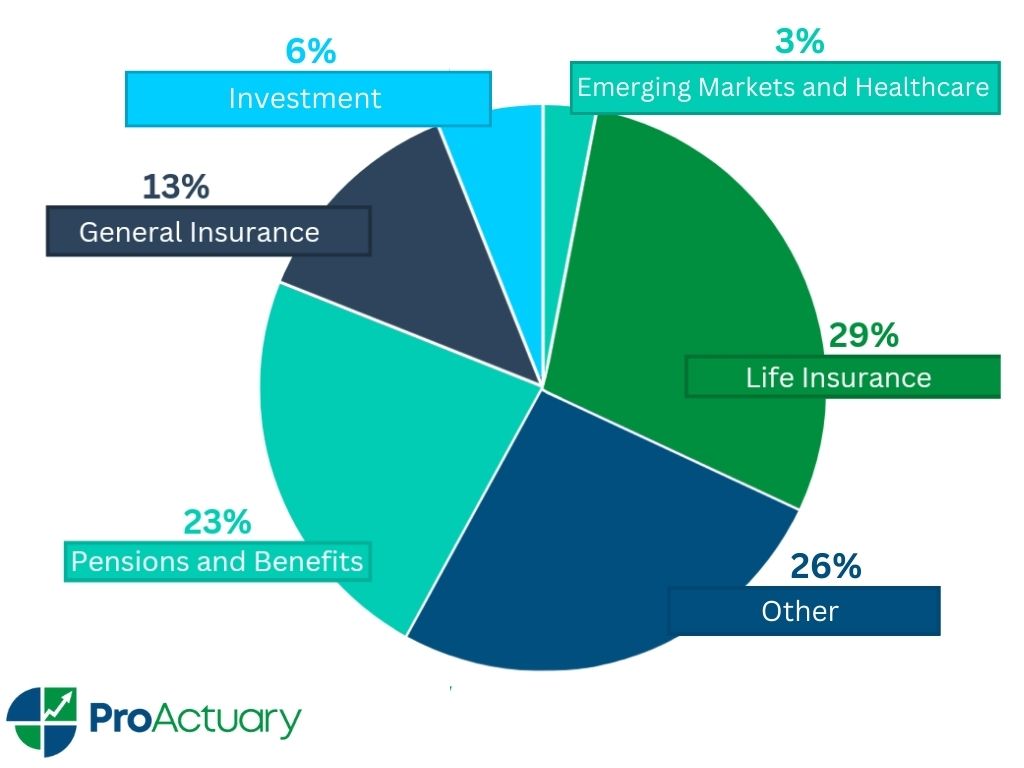
There are various different types of actuary and each type comes with a different job description. Actuaries that follow a career in the insurance industry, typically spend their time working in one of four main areas: life insurance, property and casualty insurance, retirement benefits or health insurance.
- Life insurance actuaries help develop annuity and life insurance policies for individuals and groups by creating estimates of how long someone will live.
- A property and casualty insurance actuary’s job responsibility is to work with insurance products in the property and casualty field, which includes car, homeowners, medical malpractice, or employment compensation insurance.
- Pension actuaries work with retirement plans, such as 401(k)s and defined benefit plans. They make sure the pension funds can cover their members’ retirement benefits.
- A health insurance actuary’s job description is to help develop long-term care and health insurance policies by predicting expected costs of providing care under the terms of an insurance contract.
Actuaries also have the option of moving into related fields such as risk management, investment banking, or management consulting. Some actuaries also choose to pursue additional certifications, such as the Chartered Enterprise Risk Analyst (CERA), to further specialize in the area of risk management and become an Enterprise Risk Manager.
There are many opportunities for advancement in the actuarial career. Actuaries who possess the necessary mindset and skill set can climb the corporate ladder and eventually reach leadership positions in their companies. Some actuaries eventually become chief actuary at their firm.
Actuary Job Description Template
We have also created an actuary job description pdf template outlining the key responsibilities, requirements and skills and qualifications for an actuary. This may be useful for you if you are a hiring manager seeking to hire an actuary. This pdf template can be downloaded from here.



