5 Key Subjects Required for Actuarial Science: An Academic Guide
Embark on a journey through the essential subjects required for actuarial science, a field that combines mathematics, statistics, finance, and technology to shape the future of risk assessment and financial planning.
Actuaries are experts in quantifying risk; Ironically, one of the most precarious ventures they undertake is pursuing their own career path as an actuary. According to statistical data, only 10% of people who attempt at least one actuarial exam, successfully complete their journey to becoming a fellow (the most prestigious designation awarded by the IFOA.) Attaining fellowship status is often a coveted achievement among actuaries, as it frequently leads to the higher salaries that are typically associated with the profession.
The aim of this article is to shed light on Actuarial Science by exploring its key subject areas, educational prerequisites, the demanding actuarial exams, and career opportunities. By acquiring a deeper understanding of these important aspects, it will aid you in deciding whether a career as an actuary is a path that appeals to you!
The Evolving Field of Actuarial Science and Its Diverse Applications

Actuarial Science is a lesser- known field of study, but it is highly valued for its essential role in analysing and managing risk in a vast number of industries. Despite its relatively low profile, those who are familiar with it will know that it offers rewarding career opportunities for those with strong mathematical, analytical skills and an interest in finance, economics, mathematics, and statistics.
Although the field has been around for centuries, it consistently evolves as new methods and tools are developed to better understand and manage risk. Actuaries primarily worked in industries such as Insurance and Pensions, however, with the digital age advancing, actuaries are continuing to adapt by offering their valuable expertise in other industries such as Data Science and Investment Banking.
Today, the field of Actuarial Science offers professionals a diverse range of opportunities, while also making a significant impact on organisations.
Applying Actuarial Science Across Diverse Disciplines
As an actuary, your skillset needs to be as diverse as the risks you manage. From crunching numbers to understanding finance, management, and computer science, this profession demands proficiency in multiple fields to stay ahead of the curve. Let’s take a closer look at the building blocks of this diverse and rewarding profession.
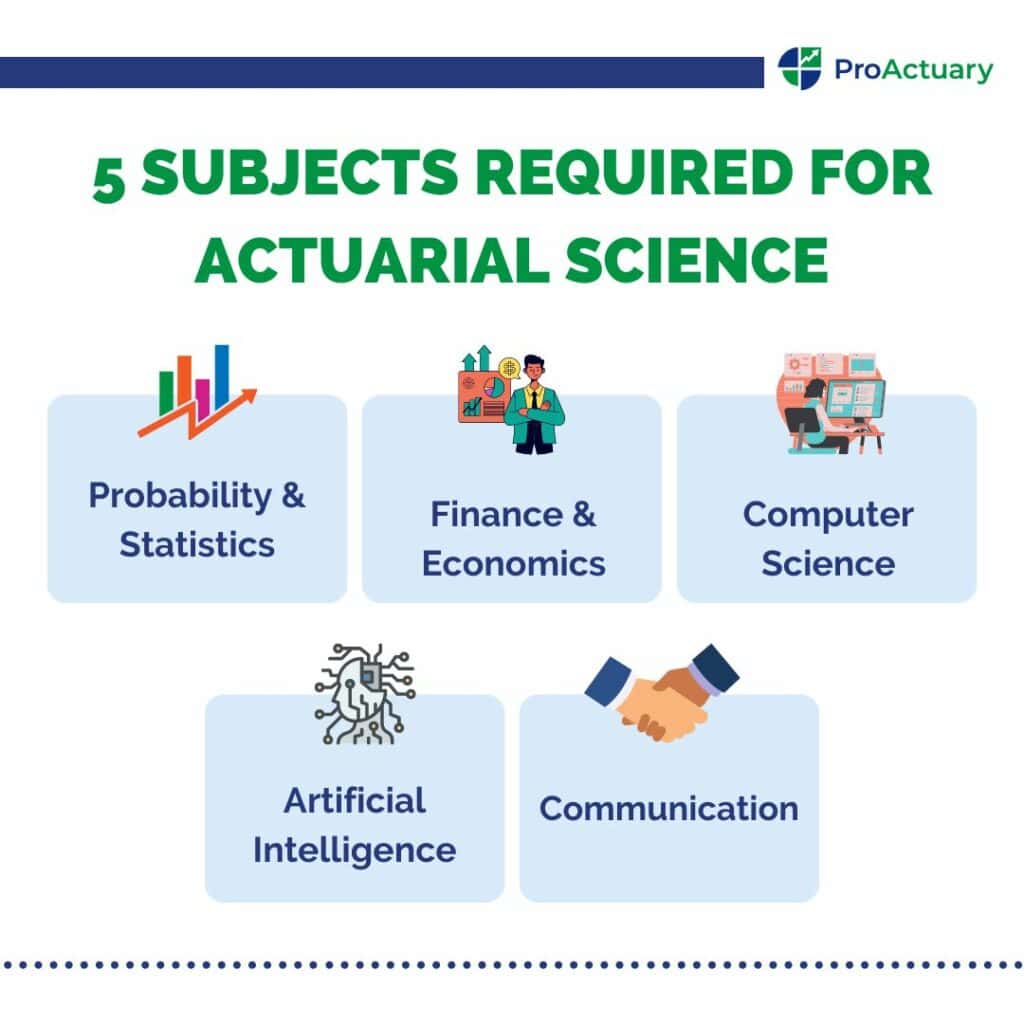
1. Probability & Statistics
Actuaries apply their skills in various industries, but their expertise remains consistent regardless of their specific area of focus. Their primary responsibility is to evaluate the likelihood and financial impact of future events. To accomplish this, they employ statistical analysis to construct models which predict the likelihood of accidents, natural disasters, and other random occurrences. These models enable actuaries to measure the risk associated with such events which is then utilised to determine insurance premiums or reserves.
In addition, actuaries use statistics to assess the accuracy and reliability of their predictive models. While these models can be useful in estimating the likelihood of specific events, they are not infallible. There is always a level of uncertainty associated with any prediction. Thus, actuaries must use statistical techniques to evaluate the potential margin of error in their models.
2. Finance & Economics
Actuaries require a comprehensive understanding of finance in addition to statistics, as they play a crucial role in developing products that help organizations manage financial risks. To achieve this, actuaries must possess a solid foundation in basic finance principles, including investment theory, financial accounting, and financial markets.
Actuaries must also have a strong grasp of the time value of money, asset pricing, and other critical factors that can affect financial markets, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. This knowledge is essential in accurately assessing the financial implications of various risks.
Furthermore, actuaries often collaborate with finance departments to convey their findings and ensure accurate data reconciliation. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of finance is a crucial component of success in the field of actuarial science.
3. Computer Science
As the actuarial field becomes more data-driven and reliant on technology, computer science is becoming increasingly important for actuaries. Actuaries have always worked with large data sets. However, With the explosion of big data in recent years, actuaries are beginning to look for more powerful tools to handle their data instead of their long run favourite, Microsoft Excel. Excel is a powerful tool for actuarial analysts, although it has its limitations when handling big data. To overcome these limitations actuaries are turning to more powerful tools such as databases and programming languages like R, Python and SAS which are specifically designed to handle big data.
In addition to technical skills, actuaries must also communicate complex results to non-actuarial stakeholders. Computer science skills can help with data visualisation and presentation making it easier to present complex information to stakeholders efficiently.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Since the emergence of an online bot ChatGPT, Artificial Intelligence has become a popular and widely discussed topic of conversation. Over the past decade, AI has become integrated into the actuarial field with many applications in areas such as fraud detection, claims processing and predictive modelling. AI can aid actuaries in analysing large and complex datasets at speed and helping them to identify patterns or anomalies that would be difficult to detect using their traditional methods. This will ultimately lead to more accurate decisions which are essential for risk management.
5. Communication
As an actuary, you’re responsible for analysing data, developing models, and designing products that help organizations manage financial risk. But none of that matters if you can’t effectively communicate your findings and recommendations. That’s why communication skills are so crucial for actuaries.
Think about it – you might be the smartest person in the room when it comes to mathematics and statistics, but if you can’t explain your analysis to your colleagues or clients in a way that they understand, it’s all for nothing. You need to be able to explain the rationale behind your recommendations, provide actionable insights, and tailor your communication style to different audiences.
And it’s not just about conveying information, either. Effective communication helps you build relationships with clients and stakeholders. You need to be able to understand their needs, preferences, and concerns and explain the benefits of your recommendations in a way that resonates with them. Without strong relationships, you won’t have the trust and confidence necessary to develop long-term partnerships that drive organizational success.
Advancing to Fellowship: The Aspirational Path in Actuarial Science
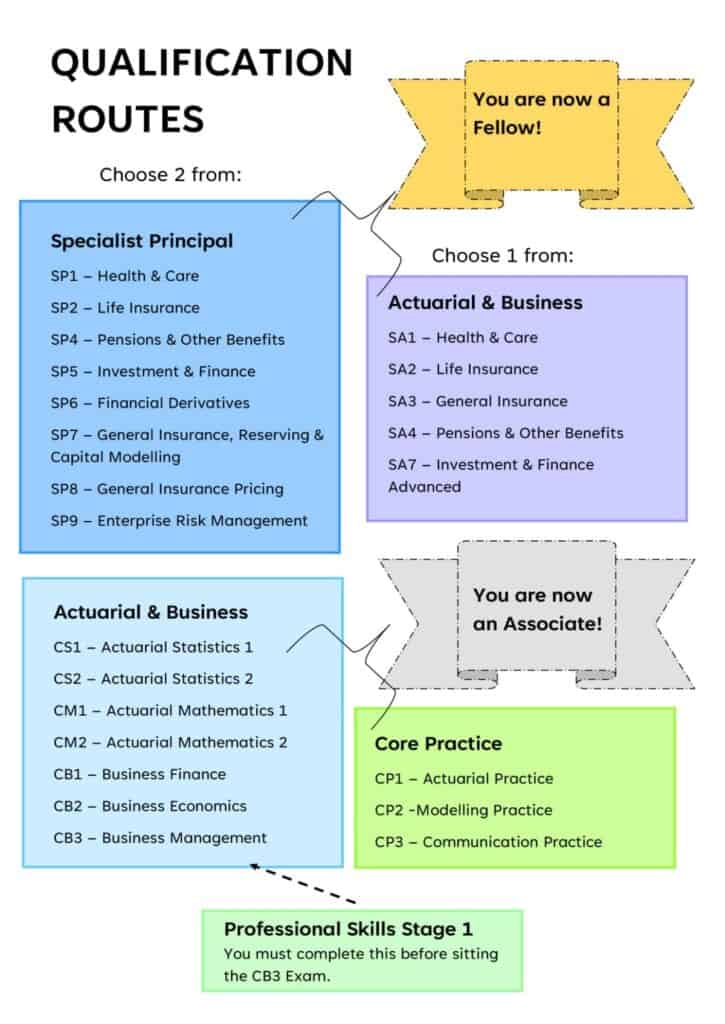
Becoming an actuary certainly isn’t for the faint of heart, it requires passing a series of rigorous exams to attain associate or fellowship status. These credentials are essential for advancing in your career and gaining recognition for your expertise and experience within the field.
Professional actuarial organizations, like the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries (IFoA) in the UK and The Society of Actuaries in the US administer the exams. To become an associate member of the IFoA, you’ll need to pass 10 exams covering a wide range of subjects, as well as completing a year of Continuing Professional Development (CPD). This program encourages professionals to continuously enhance their skills and knowledge through workshops, seminars, conferences, and networking events.
But, for most actuarial students, associate status is just the beginning. They want to specialize in their chosen area of actuarial science and pursue fellowship status – the highest level of IFoA membership. To achieve fellowship, you’ll need to pass an additional three exams and earn even more CPD credits. It’s a challenging journey but attaining fellowship status demonstrates your high level of expertise and experience in the field – a prestigious achievement indeed.
One additional point that is often overlooked is the importance of self-study and self-discipline in preparing for actuarial exams. While there are plenty of resources available, such as study materials, online courses, and study groups, the bulk of the studying will be done independently. Actuarial exams cover complex mathematical and statistical concepts, and it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of the material to pass. This requires a significant amount of self-discipline, time management, and persistence. Despite this, the effort and dedication required to become an actuary is definitely worth it.
While the path to becoming an actuary may seem daunting, the next sections of this article will explore alternative, accelerated approaches to achieving this esteemed qualification.
Think You Have What It Takes? Prove It!
So, what do you think so far? Are you up for taking on the actuarial exams? Here’s a sample of past exam questions for you to check out. Give them a try and see if you’re ready to face the challenge! Don’t worry, we’ve got the answers waiting for you at the end of this article.
Entry Requirements
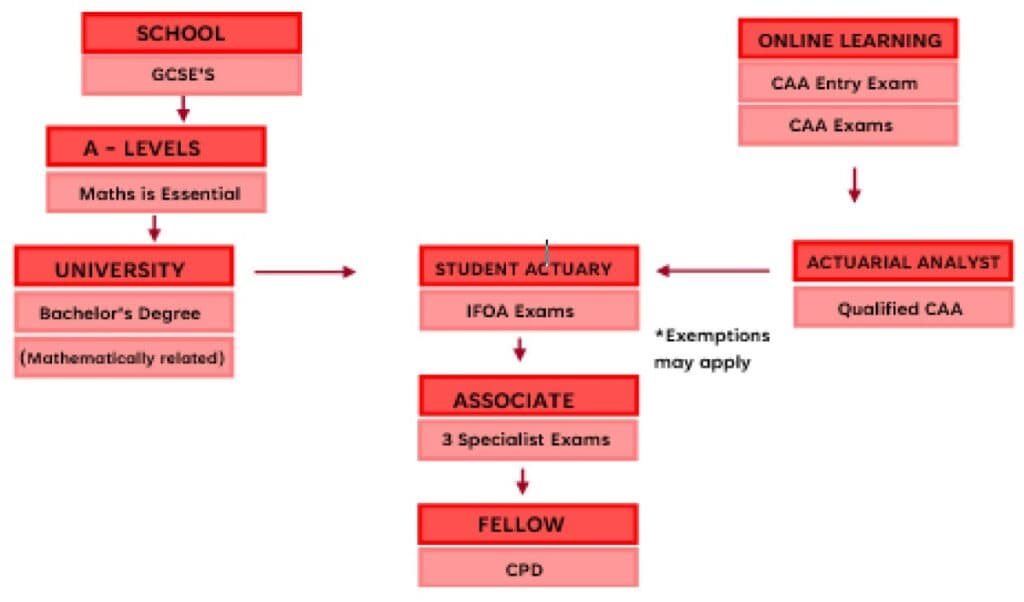
If you’ve completed a mathematical degree and are interested in becoming an actuary at the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries (IFoA), you may be eligible to join the IFoA straight away, without needing to take any additional exams. This is because a mathematical degree can provide a strong foundation in the quantitative skills needed for actuarial work.
However, if your degree isn’t in a mathematical field or you don’t meet the eligibility requirements for direct entry, another option is to take the CAA exams. These exams cover the core concepts and principles of actuarial science and can be taken independently of any formal educational program. This means that you can gain the necessary knowledge and qualifications to become an IFoA student on your own terms, regardless of your academic background.
Understanding Actuarial Science Exam Exemptions

If we have managed to pique your interest in becoming an actuary, you might be wondering if there’s a way to bypass the years of challenging exams we discussed earlier. Well, Actuarial exam exemptions may be the answer you are looking for! These exemptions are available to students who have completed relevant university courses or earned professional qualifications that are recognized by the IFoA. The IFOA website outlines 2 different routes from which exemptions can be granted. These routes are outlined on the IFOA’s exemption directory.
By demonstrating a thorough understanding of the subject matter through prior credentials, students can use these qualifications to bypass specific IFoA examinations. This significantly expedites their progression towards becoming a fully qualified actuary. Consequently, seeking exemptions not only alleviates the heavy burden of examinations, but enables actuaries to focus on other vital aspects of their professional development.
At present, 47 universities around the globe have received accreditation from the IFoA. You can find a list of these institutions on the IFoA’s official website. The accredited degrees, encompass not only actuarial science but also other fields such as mathematics, finance, business, and economics. Students who are currently pursuing or professionals who have graduated with these such degrees may be eligible for at least one exemption, making it worthwhile to explore this further!
However, at this stage you might be thinking, I have a finance degree, I’m sorted! Well unfortunately it’s not as simple as it sounds. Just because you have a degree or professional qualification, it doesn’t mean you’ll get an exemption. To qualify for an exemption, you must achieve at least 65% in the corresponding module that maps to the exemption. It’s like getting a golden ticket to Willy Wonka’s chocolate factory, but you must earn it!
For those who have completed an actuarial science degree, there’s good news. If you achieve at least 65% overall, you’ll automatically get all the exemptions that your degree offers you. This is like winning the lottery for an aspiring actuary. However, if you don’t hit that magic number, don’t despair. The IFoA will instead look at your modules individually to check if you achieved over 65% in each one. So, while getting exemptions can be a great way to accelerate your path to becoming an actuary, you need to have a strategic mindset and be prepared to put in the hard work to achieve the necessary grades.
Master’s Degree in Actuarial Science: Advanced Subjects and Career Advancement

So, you’ve come to the realization that you don’t have any exemptions and your dream of becoming an actuary may be slipping away. Fear not! There are other options available to fast-track your progress.
If you have a bachelor’s degree in a mathematical subject, you can qualify for a master’s degree in actuarial science. This allows you to achieve six or more exemptions in just one year. However, it’s important to take caution as it can be a lot to handle in one year, which is why actuarial science degrees are typically split over three years. Still, it may be a better option than trying to juggle work and studying. Ultimately, it’s up to you to decide what works best for you and your unique situation.
Answers
Now, let’s reveal the answers to the sample questions we discussed earlier. If you had a tough time with them, don’t be too hard on yourself—plenty of us have been there! We’ve all faced those perplexing moments and head-scratching situations while trying to figure out these questions.
Concluding Insights: Key Takeaways on Subjects Required for Actuarial Science

Actuaries may be experts in quantifying risk, but they sure take a big risk themselves by pursuing their career path. With only 10% of people successfully completing their journey to becoming a fellow, it’s no wonder why actuaries are such rare and coveted creatures.
The journey to becoming an actuary requires extensive knowledge in subjects such as mathematics, statistics, economics, finance, and computer science, among others. You’ll need to pass a series of rigorous exams, gain practical experience, and continuously update your skills throughout your career. But the rewards are substantial.
Actuaries are highly respected for their expertise in managing risk and analysing data, and they enjoy a challenging and rewarding career with excellent job prospects and high earning potential. So, if you’re up for the challenge and have a passion for maths and problem-solving, pursuing a career as an actuary may be the perfect path for you. Just be prepared for a wild ride filled with exams, statistics, and spreadsheets.
But hey, at least you’ll be part of the exclusive 10% club, right?




